blood analyzer laboratory mouse catecholamines|Highly sensitive LC : exporters Plasma sample E and NE were extracted using solid phase extraction, and analyzed by an in-sample ion-pairing chromatography (IPC) LC-MS/MS method, that enables the ion-pairing . webRabino Y. David Weitman, originário da Bélgica, frequentou academias talmúdicas em Israel e na França, vindo a se formar rabino pela Yeshivá Central Tomchei Temimim de .
{plog:ftitle_list}
29 de out. de 2023 · An acronym for Portable Network Graphics, PNG is a lossless file format designed as a more open alternative to the Graphics Interchange Format (GIF). Unlike JPEG, which relies on DCT compression .
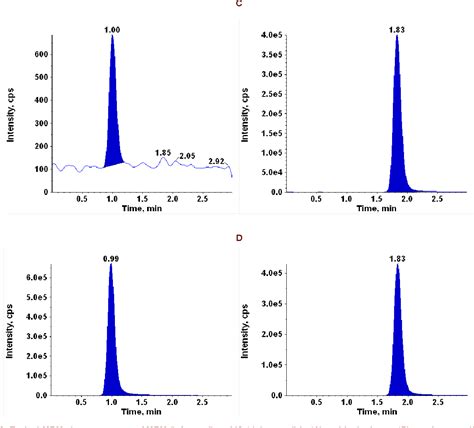
Plasma sample E and NE were extracted using solid phase extraction, and analyzed by an in-sample ion-pairing chromatography (IPC) LC-MS/MS method, that enables the ion-pairing .Implementation of a simple, efficient, and economic non-SPE sample preparation method for an analytical method for the quantification of catecholamines and metanephrines in urine using . For more than 20 years, measurement of catecholamines in plasma and urine in clinical chemistry laboratories has been the cornerstone of the diagnosis of neuroendocrine .An integrated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry approach for the ultra-sensitive determination of catecholamines in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to assess neural-immune communication.
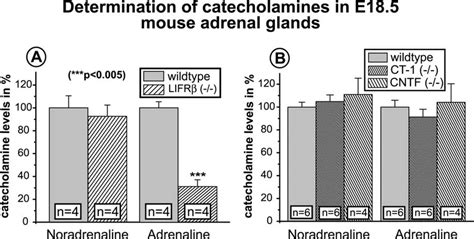
Catecholamines are routinely quantitated in blood using radioenzymatic assay or HPLC with electrochemical detection. Stress and sympathetic activation can induce . In conclusion, we modified the extraction procedure and HPLC determination of plasma catecholamine levels to enable measurements from chronically catheterized mice. .
The Clinical Chemistry laboratory tests mouse blood and urine for organ systems assessment, phenotyping confirmation, and sick mouse diagnostic purposes. The menu offers over 40 biochemical assays, cytokine analysis .The time between blood collection and the preparation of plasma is quite critical; if the time exceeds one hour, catecholamine values increase (when blood is kept at 4°C) or decrease (when left at 20°C). 1 To avoid delays in turnaround time when requesting multiple tests on frozen samples, please submit separate frozen specimens for each test . The test procedure itself is relatively straightforward. For a blood test, a healthcare professional will draw a blood sample from a vein in the arm. Urine tests often require a 24-hour collection, where the patient collects all urine produced over a full day in a special container provided by the laboratory. Dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine are physiologically active molecules known as catecholamines. Catecholamines act both as neurotransmitters and hormones vital to the maintenance of homeostasis through the autonomic nervous system. Physiologic principles of catecholamines have numerous applications within pharmacology. Pheochromocytoma is a .
False-negatives and false-positives occur. Since a 24-hour urine collection represents a longer sampling time than a random, or symptom-directed serum sample, and because catecholamine secretion by pheochromocytomas is intermittent, the 24-hour urine test may detect some cases missed by a blood or random urine level. The three catecholamines are epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine, and dopamine. Catecholamines are more often measured with a urine test than with a blood test. Alternative Names. Norepinephrine - blood; Epinephrine - blood; Adrenaline - blood; Dopamine - blood. How the Test is Performed. A blood sample is needed. How to Prepare for the TestIf this is not possible for medical reasons, contact the laboratory and discuss whether a shorter drug-withdrawal period may be possible in a particular case. 2. . withdraw and discard a minimum of 3 mL of blood to remove the saline out of the catheter. . Schmedes A. Highly sensitive LC-MS/MS analysis of catecholamines in plasma. Clin . Symptoms of Abnormal Catecholamine Levels . Abnormal catecholamine levels are those that are excessively high or low. Both situations cause symptoms. Generally speaking, high levels of certain catecholamines cause high blood pressure leading to headaches, sweating, heart pounding, chest pain, and anxiety.
For a blood test, a nurse will take a sample of your blood and send it to a lab. For infants and very young children, the doctor may use a tool called a lancet to prick the skin.
Measurement of plasma catecholamines in small samples from mice

Highly sensitive LC
Not recommended for the evaluation of pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma. Use to evaluate clinical symptoms of excess catecholamine secretion. For the assessment of pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma, refer to Metanephrines, Plasma (Free) (0050184) or Metanephrines Fractionated by HPLC-MS/MS, Urine (2007996). ||Thoroughly mix entire collection (24-hour or .This test measures the levels of catecholamines in your blood. The catecholamine hormones are epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine. Epinephrine is also called adrenalin. Catecholamines are made in the adrenal glands. They are released when you have physical or emotional stress. These hormones have many functions in the body.
Blood and urine samples are commonly used for catecholamine analysis. Blood samples are often collected via venipuncture, while urine samples are collected over a 24-hour period for accurate measurement. . These values may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and testing methods used. Abnormal results should always be interpreted in .
Article Stability of catecholamines in whole blood: influence of time between collection and centrifugation was published on February 1, 2021 in the journal Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM) (volume 59, issue 2).For the recommended first-tier laboratory test for pheochromocytoma, order either:-PMET / Metanephrines, Fractionated, Free, Plasma . draw 10 mL of blood into the chilled 10 mL catecholamine tube containing EDTA-sodium metabisulfite solution. A 6 mL pink top EDTA-metabisulfite tube is an acceptable substitute. . Schmedes A. Highly sensitive . To test a person’s catecholamine levels, a doctor will order a blood or urine test. A person having a catecholamine urine test will need to collect their urine in a bottle over the course of 24 .
A catecholamine test is done to help diagnose a tumor in the adrenal glands called a pheochromocytoma. Catecholamine levels in the blood can change quickly, so it may be hard to find high values in a single blood sample. But a special compound, metanephrine, may be found in the blood, which may mean a pheochromocytoma is present.The Endocrine Society recommends that a test for plasma free metanephrine or urine metanephrine be used to help detect the presence of phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas (catecholamine-secreting tumours). Urine and/or blood tests for catecholamines may be used to help confirm or rule out the presence of these tumours.For the analysis of catecholamines and their metabolites in urine or plasma, the ALEXYS™ Clinical Analyzer based on HPLC with electrochemical detection (LC/ECD) provides a robust and sensitive method. The ALEXYS Analyzer is compatible with all major clinical kits for sample preparation and analysis to assure standardized catecholamines analysis.
Some tumors also make catecholamines. Examples of these tumors include paragangliomas (PAYR-uh-GANG-glee-OH-muhs) and pheochromocytomas (FEE-oh-KROH-moh-sy-TOH-muhs). Measuring the amount of catecholamines and metanephrines in your urine is a way to check for these tumors. Catecholamines testing may be used in follow up to plasma free metanephrines and/or urine metanephrines testing to help confirm or rule out rare tumors called pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. It also may be used to monitor for recurrence of these tumors. Pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas produce catecholamines in excess, so .This test should not be used as the first-line test for pheochromocytoma, as plasma catecholamine levels may not be continuously elevated, but only secreted during a "spell." By contrast, production of metanephrines (catecholamine metabolites) appears to be increased continuously. The recommended first-line laboratory tests for pheochromocytoma .
A blood chemistry analyzer may be used to test for many things, such as blood cell counts, therapeutic drug monitoring, illegal drug use, blood typing, protein analysis, checking thyroid function, checking for the presence of antibodies, and, when used by patients at home, for glucose or cholesterol monitoring.This private blood assessment for Metadrenalines (Urine) (Previously Catecholamines) is offered at over thirty-two private clinics across England, Scotland and Wales. Included in every test request for Catecholamines are a Doctors Referral, all .A test for catecholamines measures the amount of the hormones epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the blood. These catecholamines are made by nerve tissue, the brain, and the adrenal glands. Catecholamines help the body respond to stress or fright and prepare the body for "fight-or-flight" reactions.A test for catecholamines measures the amount of the hormones epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the blood. These catecholamines are made by nerve tissue, the brain, and the adrenal glands. Catecholamines help the body respond to stress or fright and prepare the body for "fight-or-flight" reactions. The.
The VMA Test (Vanillylmandelic Acid test) is a laboratory test that measures the levels of VMA in a person’s urine. VMA is a metabolite of catecholamines, which are hormones produced by the adrenal glands.The test is primarily used as a diagnostic tool for the detection of certain types of tumors, such as pheochromocytoma or neuroblastoma.
Even in the absence of reducing agents, catecholamines are stable in anticoagulated blood for 1 day at 20°C, 2 days at 4°C, 1 month at −20°C, and up to 1 year at −70°C, while plasma free methanephrines can be kept at 4°C for 3 days without appreciable degradation and stored at −80°C for longer duration (70, 71). Storage conditions .
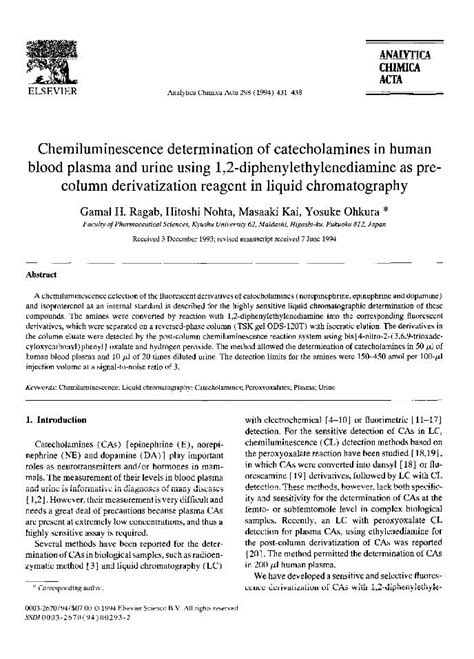
Determination of catecholamines in plasma and urine
plastic pellet moisture meter
Rukometaši Zagreba bore se za prolaz dalje u Lige prvaka: 'Već smo pokazali da možemo igrati s njima'. Rukomet.
blood analyzer laboratory mouse catecholamines|Highly sensitive LC